

|
|
|
?TAMIL NADU STATE AIDS CONTROL SOCIETY
?
Introduction:
??????????? The State AIDS Project Cell formed in 1993 was re-constituted as Tamil Nadu State AIDS Control Society (TNSACS) in 1994, with the Secretary, Health and Family Welfare Department, as the President of this Society and a senior I.A.S. Officer as the Member Secretary cum Project Director, to tackle the problem of AIDS in a more effective manner with the guidance and support of various committees and sub-committees, comprising of experts from different Fields.?
Model State in AIDS Control:
v??????? TNSACS was the first AIDS Control Society formed in the country
v??????? HIV/AIDS Awareness level among the people is very high
v??????? Number of individuals availed testing and care facilities is high.
v??????? First State, which has notified and cared large number of HIV/AIDS, affected.
Activities of TNSACS :
The main components, strategies and interventions implemented by TNSACS under the AIDS Control Programme are as follows:
|
l????? Awareness programmes and Social mobilization activities |
|
l????? Targetted Intervention Programmes through NGOs |
|
l????? Institutional and infrastructural Strengthening |
|
l????? Training and Capacity Building activities |
|
l????? STD / RTI Care and also Out-reach Service |
|
l????? Condom Promotion activities |
|
l????? Blood Safety and Voluntary Blood donation activities |
|
l????? Advocacy and Sensitization Programmes |
|
l????? Testing, Surveillance and Impact Assessment Studies |
|
l????? Low cost AIDS care and support for people living with HIV / AIDS (PLWHA) |
|
l????? Legal and General Counselling and also Helpline Services |
|
l????? Voluntary Counselling and Testing Centres to indentify HIV affected? and to provide counselling. |
?
Awareness and Social Mobilization activities:
Awareness is the key to the prevention and control of HIV / AIDS. Fear is not likely to solve any of the problems, neither is ignorance. The electronic, print and other media are fully exploited, optimising the use of the resources of TNSACS. The first phase of the IEC campaign has been a resounding success, as independent surveys of professional agencies have indicated. The campaign is already being hailed as a model for other states in the country. The emphasis has now shifted towards interpersonal communication and behaviour change communication (BCC) to ensure positive behavioural changes among the people.? The multi pronged strategy comprises of multi-media campaigns, advocacy programmes, Inter Sectoral Collabotration with all departments like? Education, Mahalir thittam, Social welfare, Local panchayat elected Representatives? etc and social mobilization activities? are implemented centrally and at decentralized level to create an awareness on HIV/AIDS.?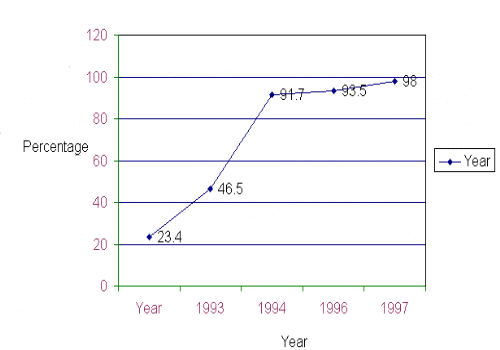
?Partnership with NGOs to reach High Risk Groups:
The involvement of NGOs in HIV/AIDS Prevention and Control Programmes aims at prevention of HIV/AIDS among Marginalised and Vulnerable Population who are at high risk.? As Tamil Nadu reached highest awareness level among General Public during the last couple of years in the entire country focus has been now shifted towards bringing behavioural changes through Targetted Interventions involving grass root level NGOs and peer educators/outreach workers/counsellors.
So far 514 NGOs are funded by Tamil Nadu State AIDS Control Society.? Currently there are 112 on going? targetted intervention programmes in the State for different risk groups such as sex workers, Truckers, Industrial Workers, Prisoners, MSM, Migrant? Workers, Injecting Drug users (IVDU), Networking with people Living with HIV/AIDS.? Monitoring and evaluation of NGO Programmes is being given top priority to facilitate positive behavioural changes.? Awareness, condom promotion and demonstrations, STD Care, Counselling, networking with People Living with HIV/AIDS are the important sub-components of these interventions.
|
Year |
No. of Interventions |
|
1994 - 1995 |
17 |
|
1995 - 1996 |
18 |
|
1996 - 1997 |
69 |
|
1997 - 1998 |
86 |
|
1998 -1999 |
106 |
|
1999 - 2000 |
41 |
|
2000 - 2001 |
61 |
|
2001 - 2002 |
52 |
|
2002 - 2003 |
64 |
|
TOTAL |
514 |
?
Blood Safety and Voluntary Blood Donation
HIV can be transmitted through blood and blood products. Therefore adequate measures have been taken for the supply of safe and tested blood.? There are 70 Government Blood Banks and also 106 Blood Banks under various sectors such as Quasi-Governmental organisations, Voluntary organisations and Private sector.? These Blood Banks are testing the donor blood for HIV, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Syphilis and Malarial infections.? Tamil Nadu State AIDS Control Society supplies Test kits, consumables and certain equipments to all Government Blood Banks at free of cost. Lab Technicians and Counsellors support to Government Blood Banks are also provided by TNSACS, besides imparting training to personnel handling Blood and Blood products.
The Tamil Nadu State Blood Transfusion Council (TNSBTC) closely monitors the activities of Blood Banks with the association of Drug Control authorities and State Health authorities.? Professional Blood donation has been banned since 1998.? Therefore all the necessary measures are taken by TNSACS to promote voluntary blood donation and ensure safe and adequate blood.? TNSACS has taken several measures for the same such as dissemination of the messages popularising the concept of Voluntary Blood Donation, provision of funds to Universities District administration, Corporations, Directorates of Collegiate and School Education, Voluntary organisations & Non-Governmental Organisations for promotional activities.? Blood Donor Clubs were formed in the Colleges with? the involvement of Universities. Financial Assistance is extended to Government? Blood Banks towards refreshments to donars and conduction of camps.? Processing of Blood components and its usage are being promoted.
?? Blood Collection data in Tamil Nadu
|
Year |
No. of units collected |
|||
|
Voluntary Donors |
Replacement Donors |
Total |
% of Voluntary Blood Donation |
|
|
1999 |
1,10,939 |
1,32,080 |
2,43,019 |
45.7% |
|
2000 |
1,51,006 |
1,52,091 |
3,03,097 |
49.7% |
|
2001 |
1,54,533 |
1,52,080 |
3,06,613 |
50.4% |
|
2002 |
2,28,902 |
1,56,455 |
3,85,357 |
59.4% |
?
??
?
?
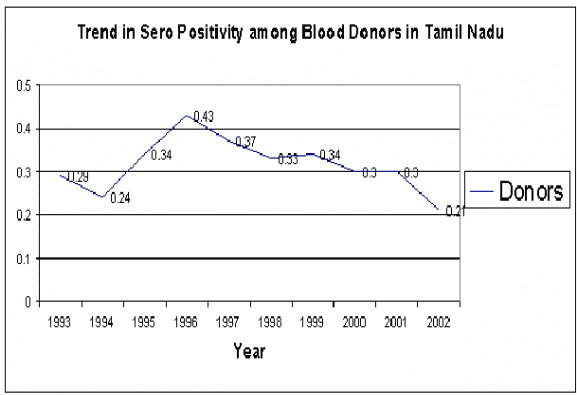
The numbers of Voluntary Blood Donors have gone up and consequently HIV Positivity among blood donors has come down to 0.28% which is less than national average.??? About 63.19% of Blood is collected from Voluntary Blood donors and proposed to increase further.
?
?Control of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
??????????? The risk of transmission and spread of HIV/AIDS among STD patients is much higher than the general population.? Therefore priority is given to STD/RTI Care and outreach activities.? There are 57 STD clinics in various Institutions including Medical College Hospitals (11), District Headquarter Hospitals and Taluk Hospitals (46).? All these STD clinics are strengthened with necessary equipment and laboratory support, including Counselling facilities.? The Drugs are supplied for the effective treatment of the patients attending these STD clinics.? Counselling is provided to the attendees in outreach camps and also at STD clinics.? Condoms are supplied to the clinic attendees free of cost.? Partners of the patients are notified for improving effectiveness of the treatment and follow up services and to reduce the risk of transmission.?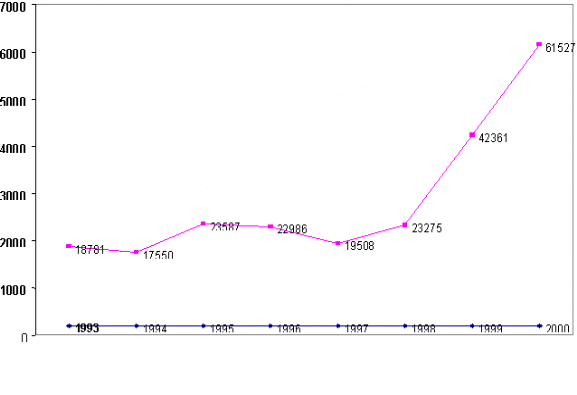
?Condom Promotion:
Top Priority is being given to promote condom usage among people, both high-risk and low risk, to prevent transmission of HIV through sexual route of transmission and unprotected sex.? Three different strategies are adopted by TNSACS as indicated below:
v?? Distribution of Free condoms (Nirodh) to the people through Health Care Institutions, STD clinics, Outreach camps and also through Non-Governmental Organisations. (NGOs)
v?? Promotion of subsidised or low priced condoms (Deluxe Nirodh) among the people in Targetted Intervention areas and non-intervention areas with the support of Non-Governmental Organisations.
v?? Promotion of condom usage and popularising the concept of safe sex and condom use through awareness and behavioural change communication.
?
|
Type of activities |
2002 - 2003 |
|
Free distribution of condoms |
0.60 Lakhs |
|
Social Marketing of low priced condoms |
1.60 Lakhs |
?
Training and Capacity Building
In order to have better service delivery system and to have institutional strengthening in private and public sector, training activities has been given due importance by making adequate provision in Action Plan to? impart training on HIV/AIDS to Medical, Para-medical and personnel of different sectors and departments.? This will positively bring capacity? building among a various stake holders for a better performance in AIDS Control efforts and also to face challenges in future.? About 4,110 individuals were trained on different aspects of HIV.
???? TRAINING PERFORMANCE DURING 2002-2003 (UP TO JANUARY 2003)
|
1.?????????? ? |
Joint Director of Medical Services |
30 |
|
2.?????????? ? |
Nodal Officers |
40 |
|
3.?????????? ? |
Trainer Training (Nurses) |
30 |
|
4.?????????? ? |
Nurses |
600 |
|
5.?????????? ? |
Medical Officers/Para Medical of AIDS Wards |
60 |
|
6.?????????? ? |
Faculty Member ITI |
600 |
|
7.?????????? ? |
NSS Co-ordinatores |
600 |
|
8.?????????? ? |
Refresher Training to Medical Officers in PHCs |
300 |
|
9.?????????? ? |
Village Health Nurses |
600 |
|
10.?????? ? |
Multipurpose Health Workers |
150 |
|
11.?????? ? |
Sector Health Nurses |
300 |
|
12.?????? ? |
ESI Medical Officers Training |
90 |
|
13.?????? ? |
ESI Nurses |
180 |
|
14.?????? ? |
ESI Para Medical Staff |
180 |
|
15.?????? ? |
Blood Bank Medical Officers |
60 |
|
16.?????? ? |
Private Medical Practioners |
600 |
Screening of HIV status of any individual is important to assess the caseload in the community. Informed consent, pre test - counselling and post test counselling, confidentiality etc. are important conditions insisted upon before the results are made known to the individuals.? For this purpose, apart from 3 Voluntary Counselling and Testing Centre (VCTCs) already available in Tamil Nadu, 11 VCTCs has been sanctioned during the year 2000 - 2001,? 19 more VCTCs has been sanctioned during the year 2001 - 2002 to increase the testing facilities, 5 VCTCs sanctined during the current? year 2002 - 2003 total? to? 42 centres which covers? all the districts of the State.
Year |
No.of persons availed Testing facilities |
Found Positive for HIV |
|
2002 - 2003 |
35521 |
4976 |
Surveillance System to assess Trends:
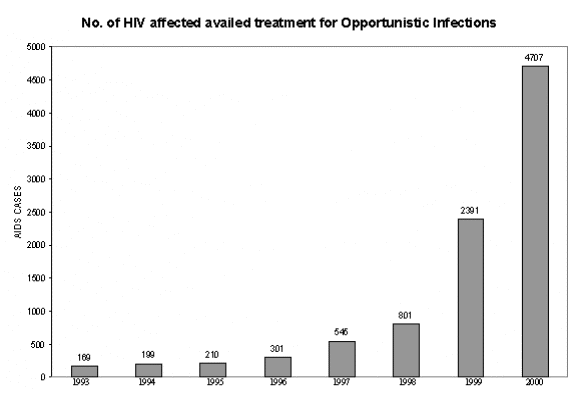
Surveillance system is essential to assess the trend in the spread of HIV infection among both High risk and low risk population and the same is being strengthened every year.? There are 24 sentinel surveillance survey sites in the State during 2002.? The latest survey reveals that the HIV sero-positivity among STD patients is 11.2% and among antenatal mothers it is 1.1%.? HIV prevalence among Injecting Drug Users (IDUs) and Homosexuals are 33.8% and 2.40% respectively.? In order to obtain more reliable information about the trend of infection in all the areas the number of sentinel sites will be increased further during this year with the requisite supply of equipment.? Behavioural Surveillance Survey done by TNSACS reveals increased condom usage, increased risk perception and reduced sexual risk behaviour.
 ?
?
Programmes for Youth/adolescence and Vulnerable:?
??????? School AIDS Programme was implemented in 1740 schools in entire state targetting the students studying 9th and 10th standards, to create an awareness levels among them and also to sensitize them on the consequences of HIV/AIDS.
??????? College AIDS talk programme is being implemented in selected colleges to address this vulnerable group.? The concept of "Red Ribbon clubs" was evolved with the involvement of student groups to act as a forum for discussion of various issues relating to HIV/AIDS.
??????? Programmes were conducted to sensitize vulnerable groups such as prisoners, hill people, slum dwellors and women working in industries.
Year |
No. of Schools covered |
No. of Colleges covered |
|
1997 - 1998 |
350 |
- |
|
1999 - 2000 |
780 |
- |
|
2000 - 2001 |
725 |
60 |
|
2001 - 2002 |
435 |
- |
|
2002 - 2003 |
1740 |
- |
Family Health Awareness Campaigns:
??????????? TNSACS has implemented three phases of Family Health Awareness Campaign (FHAC) in the State with the support from NACO, Govt. of India to identify the STD and RTI cases and to treat them with syndromic management, basically to eliminate aggravating factors such as STD and RTI which contributes for faster spread of HIV/AIDS.? The campaign mode approach adopted by TNSACS to reach the needy at their doorsteps has paved a way for identifying the vulnerable groups in rural and urban areas.???????
??????????? Total No. of? STD cases identified and treated during II nd? and 3rd? round are given below.
Phase |
Total Number of STDs treated |
||
|
II |
97,292 |
5,14,488 |
6,11,780 |
|
III |
1,36,355 |
5,26,975 |
6,63,330 |
TOTAL |
2,33,647 |
10,41,463 |
1,27,5110 |
Voluntary Counselling and Testing Centres:
??????????? Voluntary Counselling and Testing Centers are functioning in all Districts Head Quarters in State? apart from the city? for screening the HIV status of any individual with informed concerned, pretest counselling and post test counselling confidentiality are done in these centers functioning in Tamil Nadu.
Prevention of Mother to Child Programme:
??????????? Mother to child transmission is by for the most significant route of transmission of HIV infection in children below the age of 15 years.? The broad strategies and guiding principle would be to provide rationale intervention for the prevention of mother to child transmission, care of mothers and children affected with HIV and reducing their vulnerability.? The Programme is implemented in 47 Hospitals in Tamil Nadu.
Financial Performance:
??????????? The Grant in aid received from National AIDS Control Organisation, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare and expenditure incurred are given below.
Year |
Allocation approved (Rs. in Lakhs) |
Expenditure incurred (Rs. in Lakhs) |
|
1992 - 93 |
145.42 |
0.88 |
|
1993 - 94 |
153.26 |
78.50 |
|
1994 - 95 |
277.44 |
227.79 |
|
1995 - 96 |
650.00 |
679.73 |
|
1996 - 97 |
1743.94 |
1330.41 |
|
1997 - 98 |
2000.00 |
1688.84 |
|
1998 - 99 |
1595.13 |
1386.60 |
|
1999 - 2000 |
1571.99 |
1400.13 |
|
2000 - 2001 |
1000.00 |
769.15 |
|
2001 - 2002 |
1300.88 |
1621.11 |
|
2002 - 2003 |
1500.67 |
680.52 (Upto Jan03) |
Component-wise expenses during 2002-03 are given below:
?(Rs.in lakhs)???
|
Sl. No. |
Component |
Amount approved |
? Expenditure ? |
|
1 |
Targeted Interventions, STD Control and Condom Promotion |
511.42 |
200.81 |
|
2 |
Awareness Programmes, Blood Safety and Testing |
605.09 |
260.79 |
|
3 |
Institutional Strengthening (Surveillance & Training) |
214.05 |
89.37 |
|
4 |
Low cost AIDS Care, Support to HIV affected |
145.11 |
125.26 |
|
5 |
Intersectoral Collaboration and Co-ordination |
25.00 |
4.29 |
TOTAL |
1500.67 |
680.52 |
|
?????
?